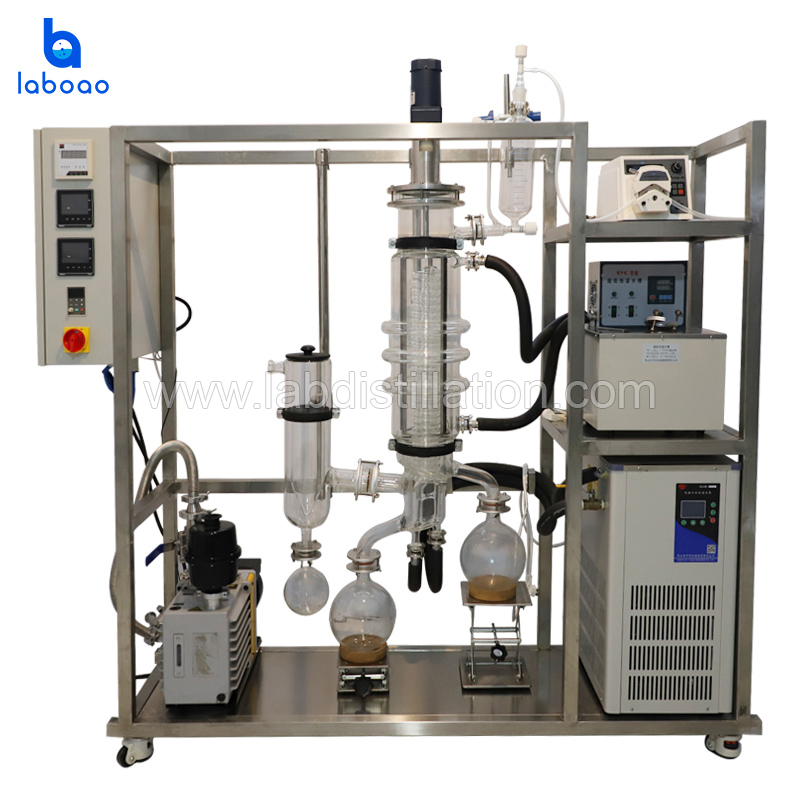
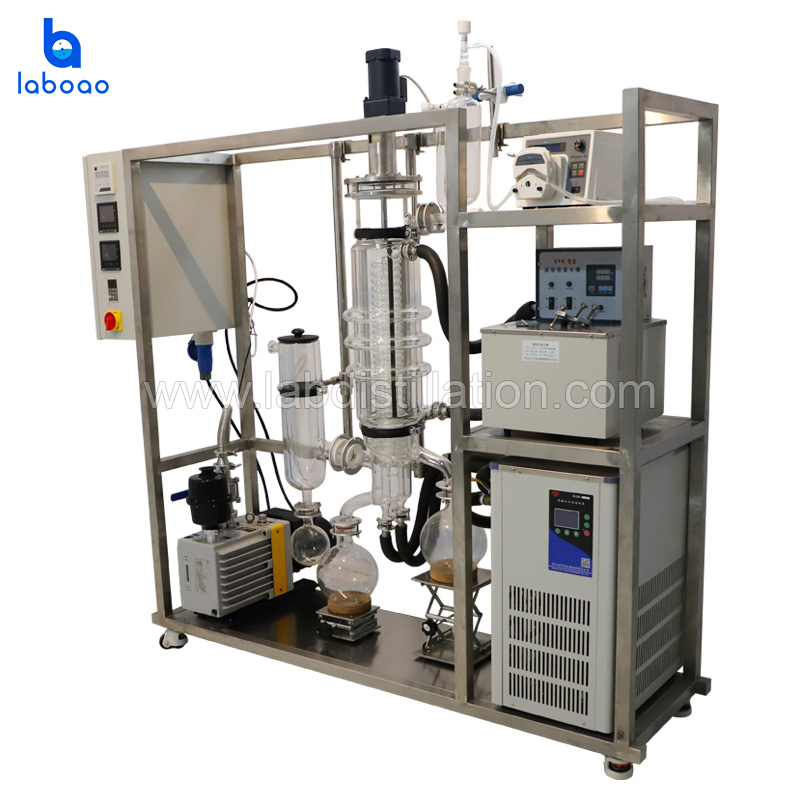
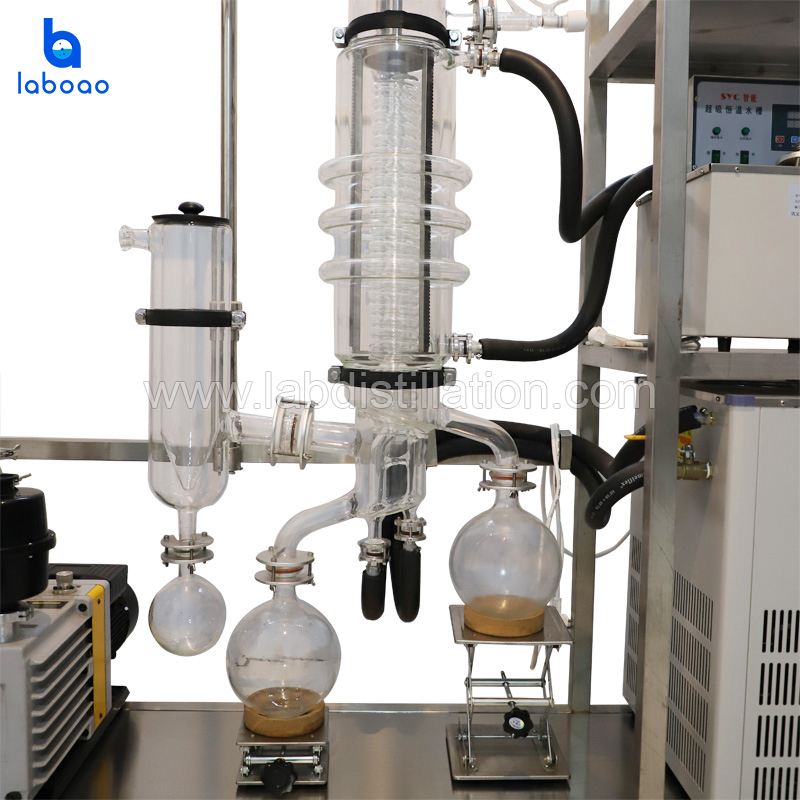
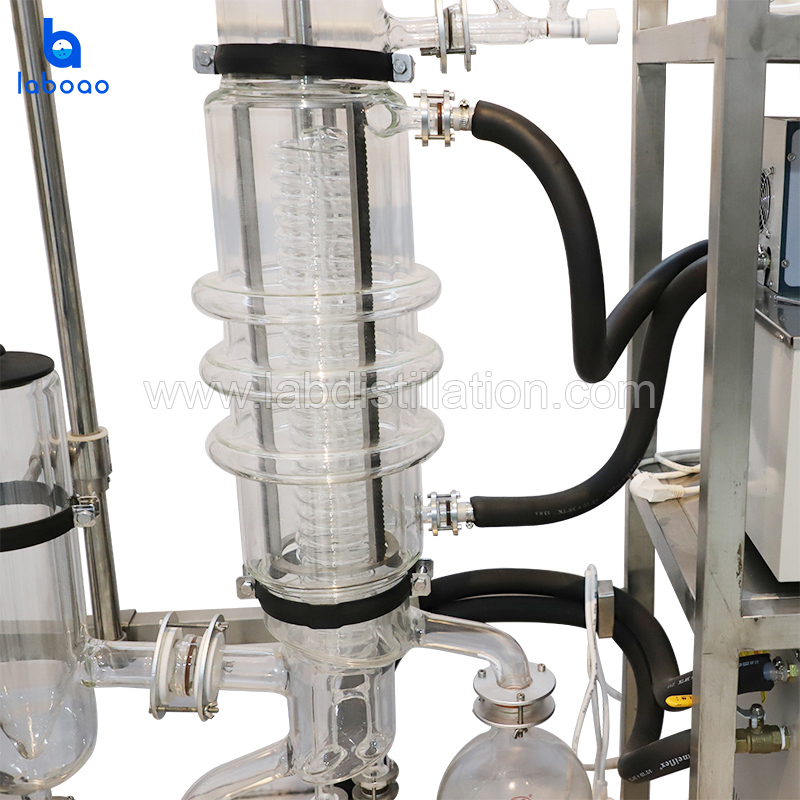
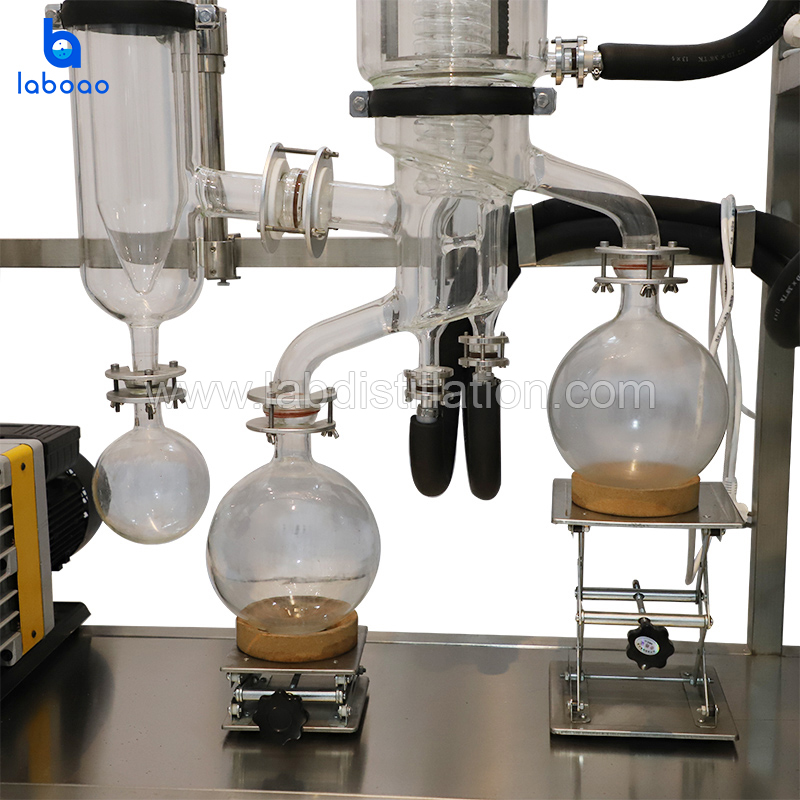
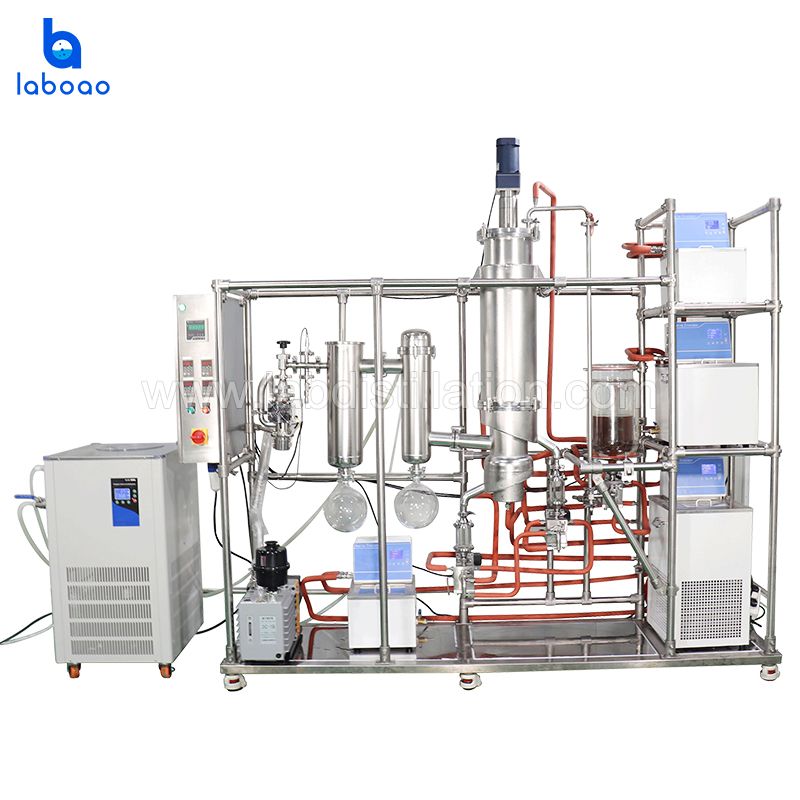
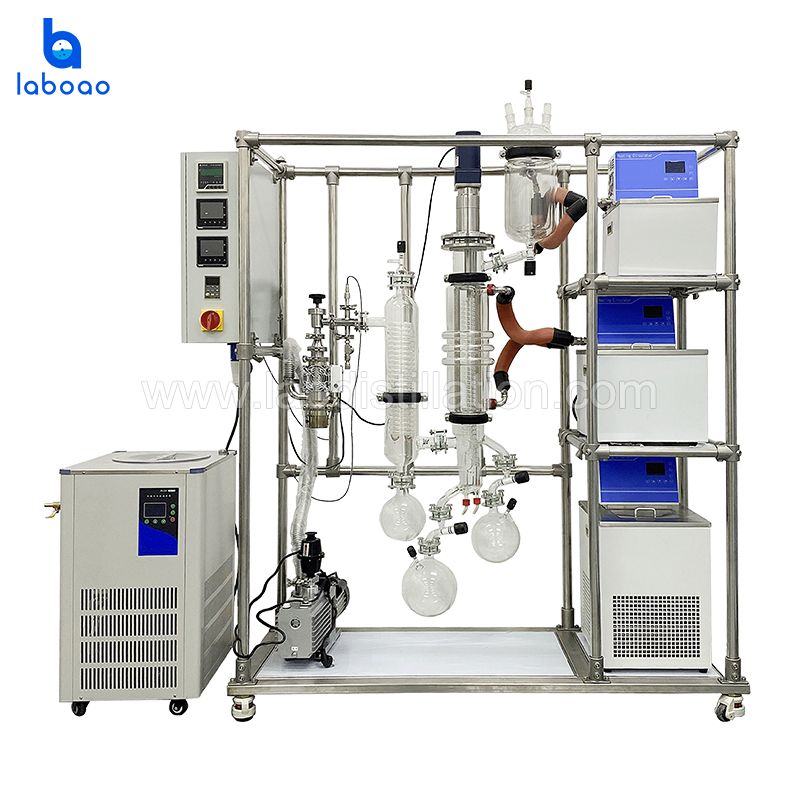
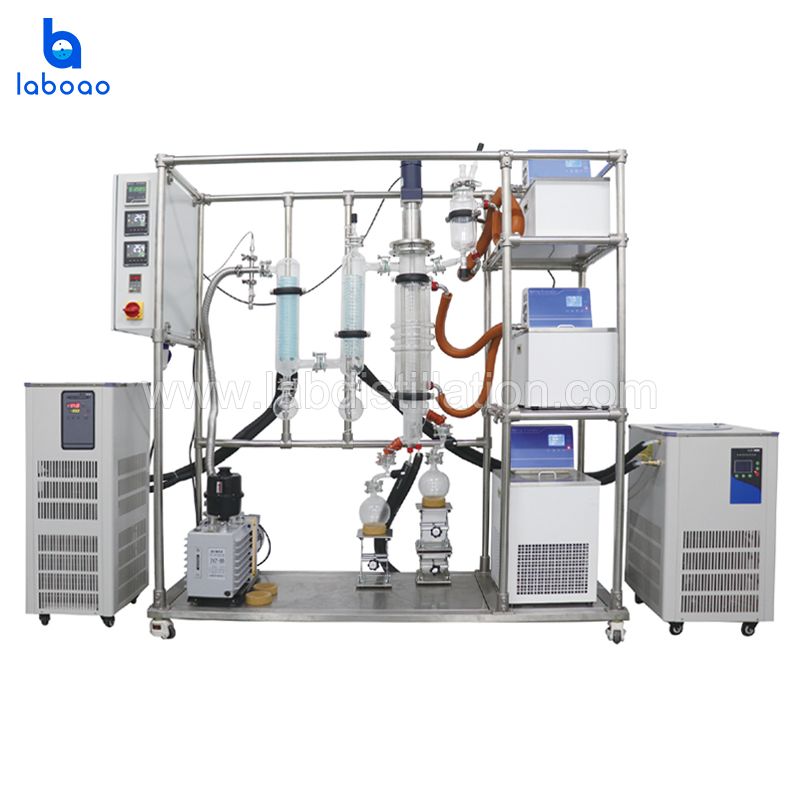
FEATURES
1. The distillation temperature is low, and molecular distillation is operated at temperatures far below the boiling point. As long as there is a temperature difference, separation can be achieved. This is the essential difference between molecular distillation and conventional distillation.
2. The vacuum of distillation is high, and the internal vacuum of the molecular distillation device can be obtained. Usually molecular distillation operates at a very low pressure, so the material is not easily oxidized.
3. Distilled liquid film thin, high heat transfer efficiency.
4. The heating time of the material is short, and the distance between the heated liquid surface and the cooled condensation surface is less than the average free path of the light molecule, so the light molecules escaping from the liquid surface reach the condensation surface almost without collision. Therefore, the heating time of the distillation material is short, and the stay time at the distillation temperature is generally between seconds and tens of seconds,
which reduces the chance of thermal decomposition of the material.
5. More separation, molecular distillation can separate conventional materials that are not easily separated.
6. There is no boiling bubbling phenomenon. Molecular distillation is free evaporation on the surface of the liquid layer. lt is carried out at low pressure and there is no dissolved air in the liquid. Therefore, the entire liquid can not be boiled during distillation and there is no bubbling phenomenon.
7. Non-toxic, harmless, no pollution, no residue, can be pure and safe products, and the operation process is simple, less equipment. Molecular distillation can separate materials that are not easily separated by conventional distillation.
8. Molecular distillation equipment cost good, and the molecular distillation device must ensure that the system pressure reaches a high degree of vacuum. The requirements for material sealing are high, and the distance between the evaporating surface and the condensing surface must be moderate. The equipment is difficult to process and the cost is high.
9. The energy consumption of the product is small, because the total thermal loss of molecular distillation is less, and because of the unique structure of the molecular distillation device, the internal pressure is extremely low, and the internal resistance is much smaller than that of conventional distillation so it can greatly save energy consumption.
Advantage:
From the above characteristics of molecular distillation technology, it can be seen that it has the following obvious advantages over conventional distillation technology in practical industrial applications:
1. Molecular distillation provides the best separation method for the separation of high boiling point, thermal sensitivity and oxidizing materials. Because molecular distillation operates at temperatures far below the boiling point of the material, and the material stays for a short time;
2. Molecular distillation can be extremely effective in removing substances in liquids such as organic solvents, odors, etc., which is a very effective method for the decolorization of liquids after solvent extraction;
3. Molecular distillation may selectively evaporate the product of the purpose, remove other impurities, and separate more than two substances at the same time through multistage separation;
4. The fractionation process of molecular distillation is a physical process, which can well protect the separated material from pollution and infringement.
SPECIFICATIONS
Model | LMD-60A | LMD-80A | LMD-100A | LMD-150A | LMD-200A | LMD-230A |
Effective evaporator area (m²) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.5 |
Barrel diameter (mm) | 60 | 80 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 230 |
Feeding volume (L) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Processing flow (kg/h) | 0.1-2.0 | 0.3-4.0 | 0.5-5.0 | 1.0-8.0 | 1.5-10.0 | 2.0-15.0 |
Motor power (W) | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 200 | 200 |
Blade material | SS316L +PTFE |
Lifting for receiving flask | YES (2 SETS) |
Cold trap volume (L) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Operation temperature | RT ~300°C |
Temperature display meter | Omron brand |
Vacuum degree accuracy | 0.0001Pa |
Frame material | SS304 (SS316 is optional) |
Customized | YES |
Application:
Molecular distillation is used industrially for purification of oils. It is also used to enrich borage oil in γ-linolenic acid (GLA) and also to recover tocopherols from deodorizer distillate of soybean oil (DDSO).
Typical Applications
Fine Chemicals
Separation of nitric acid from organic high boiling liquids
Separation of butane (butyne) diol from high boiling liquids
Recovery of methanol from high boiling liquids
Recovery of xylenol (dimethylphenol) from a purification solution
Removal of hexane from PP and PE waxes
Drying of salt via the evaporation of water and solvent
Separation of phenol from bituminous coal pitch
Distillation of starting products for the production of insecticides
Separation of byproducts in the production of synthetic fibers
Polymers
Distillation of TDI, HDI and MDI (isocyanates)
Final removal of toluene from epoxy resin
Separation of THF from polymers
Distillation of trimethylpropane from high boiling liquids
Recovery of solvents from synthetic resin production
Lactic Acid, starch and sugar
Upgrading and distillation of lactic acid
Upgrading of tartaric acid derivatives
Concentration of sweetening agents
Concentration of modified starch
Pharmaceuticals
Concentration of active ingredient solutions
Distillation of pharmaceutical substances
Upgrading of substances for artificial feeding
Oleochemicals, Fatty Acids,Biodiesel
Separation of dioxin from surfactants
Removal of free fatty acids from mon, di and triglycerides
Distillation of monoglycerides
Distillation of fatty acids from tall oil
Distillation of fatty acid methyl esters
Separation of residual glycerine from residues in biodiesel production (glycerine dryer)
Miscellaneous
Drying of industrial sludge
Drying & pre-concentration of municipal sewage sludge
Drying of hydroxide sludge
Drying of inorganic salt solutions
Drying of preliminary and intermediate products from chemical industry
Drying of suspensions, pastes and moist solids into powder
Drying of lubricants for forging industry